Archive
Consumer Buying Behavior
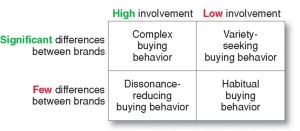
Types of buying behavior
There are four different types of buying behavior based on the types of products that are intended to be purchased.
Stimulus-Response Model
The stimulus–response model is a characterization of a statistical unit (such as a neuron) as a black box model, predicting a quantitative response to a quantitative stimulus. In this model, marketing and other stimuli enter the customers “black box” and produce certain responses. Marketing management must try to work out what goes on the in the mind of the customer – the “black box”.
Marketing and other stimuli: A consumer is confronted with a stimulus in the environment. This stimulus could be of two kinds;
a) One that is presented by the marketer through the marketing mix or the 4Ps, product, price, place and promotion;
- product: attributes, features, appearance, packaging etc.
- price: cost, value, esteem (prestige)
- place: location and convenience, accessibility
- promotion: advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, publicity, direct marketing.
b) The other that is presented by the environment, and could be economic, technological, political and cultural.
Buyer’s black box: The stimulus that is presented to the consumer by the marketer and the environment is then dealt with by the buyer’s black box. The buyer’s black box comprises two sub components, viz., the buyer’s characteristics and the buyer decision process.
The Buyer’s characteristics influence how he or she perceives the stimuli; the decision-making process determines what buying behavior is undertaken.
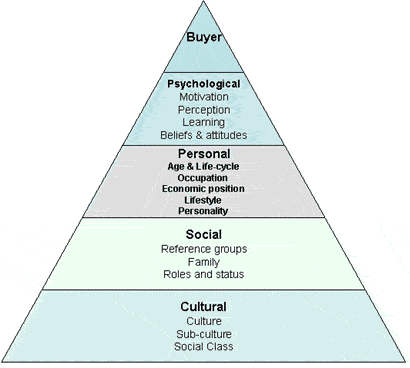
The first stage of understanding buyer behavior is to focus on the factors that determine the “buyer characteristics” in the “black box”. These can be summarized as follows:
Customers go through a five-stage decision-making process in any purchase. This is summarized in the diagram below:
 This model is important for anyone making marketing decisions. It forces the marketer to consider the whole buying process rather than just the purchase decision (when it may be too late for a business to influence the choice!)
This model is important for anyone making marketing decisions. It forces the marketer to consider the whole buying process rather than just the purchase decision (when it may be too late for a business to influence the choice!)
The model implies that customers pass through all stages in every purchase. However, in more routine purchases, customers often skip or reverse some of the stages.
The buying process starts with need recognition. At this stage, the buyer recognizes a problem or need.
An “aroused” customer then needs to decide how much information (if any) is required. If the need is strong and there is a product or service that meets the need close to hand, then a purchase decision is likely to be made there and then. If not, then the process of information search begins.
A customer can obtain information from several sources:
• Personal sources: family, friends, neighbors etc
• Commercial sources: advertising; salespeople; retailers; dealers; packaging; point-of-sale displays
• Public sources: newspapers, radio, television, consumer organisations; specialist magazines
• Experiential sources: handling, examining, using the product
The usefulness and influence of these sources of information will vary by product and by customer.
In the evaluation stage, the customer must choose between the alternative brands, products and services. An important determinant of the extent of evaluation is whether the customer feels “involved” in the product. By involvement, we mean the degree of perceived relevance and personal importance that accompanies the choice.
The final stage is the post-purchase evaluation of the decision. It is common for customers to experience concerns after making a purchase decision. This arises from a concept that is known as “cognitive dissonance”. The customer, having bought a product, may feel that an alternative would have been preferable. In these circumstances that customer will not repurchase immediately, but is likely to switch brands next time.
To manage the post-purchase stage, it is the job of the marketing team to persuade the potential customer that the product will satisfy his or her needs. Then after having made a purchase, the customer should be encouraged that he or she has made the right decision.
Consumer Buying Behavior
Consumer buying behavior can be defined as the way in which consumers or buyers of goods and services tend to react or behave when purchasing products that they like. Buyers tend to exhibit different types of buying behavior when they are in the process of purchasing goods and services and the behaviors witnessed are influenced by the type of product he/she wants to buy. Consumer buying behavior involves a long process where the buyer has to identify the product, study well its features, the pros and the cons and lastly deciding on whether to purchase it or not.
Consumer buying behavior would make a certain buyer to purchase product A as opposed to product B or whether to purchase a certain product or leave it alone and all that is as a result of the buying decisions made by the buyer as to whether the product suits his/her needs and requirements.
Factors affecting consumer buying behavior
Cultural factors affecting consumer buying behavior:
Cultural factor divided into three sub factors (i) Culture (ii) Sub Culture (iii) Social Class
Culture: – The set of basic values perceptions, wants, and behaviors learned by a member of society from family and other important institutions. Culture is the most basic cause of a person’s wants and behavior. Every group or society has a culture, and cultural influences on buying behavior may vary greatly from country to country.
Sub Culture: – A group of people with shared value systems based on common life experiences and situations. Each culture contains smaller sub cultures a group of people with shared value system based on common life experiences and situations. Sub culture includes nationalities, religions, racial group and geographic regions. Many sub culture make up important market segments and marketers often design products.
Social Class: – Almost every society has some form of social structure; social classes are society’s relatively permanent and ordered divisions whose members share similar values, interests and behavior.
Social factors affecting consumer buying behavior:
A consumer’s behavior is also influenced by social factors, such as the (i) Groups (ii) Family (iii) Roles and status.
Groups: – Two or more people who interact to accomplish individual or mutual goals. A person’s behavior is influenced by many small groups. Groups that have a direct influence and to which a person belongs are called membership groups. Some are primary groups includes family, friends, neighbors and coworkers. Some are secondary groups, which are more formal and have less regular interaction. These include organizations like religious groups, professional association and trade unions.
Family: – Family members can strongly influence buyer behavior. The family is the most important consumer buying organization society and it has been researched extensively. Marketers are interested in the roles, and influence of the husband, wife and children on the purchase of different products and services.
Roles and Status: – A person belongs to many groups, family, clubs, and organizations. The person’s position in each group can be defined in terms of both role and status. For example, M & X plays the role of father, in his family he plays the role of husband, in his company, he plays the role of manager, etc. A Role consists of the activities people are expected to perform according to the persons around them.
Personal factors affecting consumer buying behavior: – It includes
Age and Life cycle Stage: – People change the goods and services they buy over their lifetimes. Tastes in food, clothes, furniture, and recreation are often age related. Buying is also shaped by the stage of the family life cycle.
Occupation: – A person’s occupation affects the goods and services bought. Blue collar workers tend to buy more rugged work clothes, whereas white-collar workers buy more business suits. A Co. can even specialize in making products needed by a given occupational group. Thus, computer software companies will design different products for brand managers, accountants, engineers, lawyers, and doctors.
Economic situation: – A person’s economic situation will affect product choice
Life style: – Life Style is a person’s Pattern of living, understanding these forces involves measuring consumer’s major AIO dimensions, i.e. activities (Work, hobbies, shopping, support etc.) interest (Food, fashion, family recreation) and opinions (about themselves, Business, Products)
Personality and Self-concept:- Each person’s distinct personality influence his or her buying behavior. Personality refers to the unique psychological characteristics that lead to relatively consistent and lasting responses to one’s own environment.
Psychological factors affecting consumer buying behavior:-
Motivation: – Motive (drive) a need that is sufficiently pressing to direct the person to seek satisfaction of the need.
Perception: – The process by which people select, Organize, and interpret information to form a meaningful picture of the world.
Learning: – Changes in an individual’s behavior arising from experience.
Beliefs and attitudes: – Belief is a descriptive thought that a person holds about something. Attitude, a Person’s consistently favorable or unfavorable evaluations, feelings, and tendencies towards an object or idea
Consumer Buying Behavior
Introduction
The purpose of a business is to create and keep customers. Customers are created and maintained through marketing strategies. And the quality of marketing strategies depends on knowing, serving, and influencing consumers. The study of consumer behavior enables marketers to understand and predict buying behavior of consumers in the marketplace. It is concerned not only with what consumers buy, but also with why they buy it, when and where and how they buy it, and how often they buy it, and also how they consume it & dispose it. Consumer research is the methodology used to study consumer behavior; it takes place at every phase of the consumption process: before the purchase, during the purchase, and after the purchase. Research shows that two different buyers buying the same product may have done it for different reasons; paid different prices, used in different ways, have different emotional attachments towards the things and so on.
Literature Review
Posting summary of some of the research papers gone through:
Computers in Human Behavior
This research paper talks about factors that affect consumer intention toward online buying behavior such as beliefs (reciprocity, reputation, and trust) and vendor creativity collectively influences user satisfaction toward websites and vendors; trust and vendor creativity have a salient effect on behavioral intention toward online group buying. Empirical data for this research is obtained using an online survey that has several advantages over traditional paper-based surveys, such as fast response time, cost-efficiency, and an absence of geographical boundaries. The research model is assessed using partial least squares (PLS) analysis. This method is an appropriate analytical tool in this case because it has minimal demands on measurement scales, sample size, and residual distributions.
The results show that a positive customer experience with online group buying creates trust and gains experience about products or services. The intention to engage in online group buying is predicted collectively by consumer satisfaction, trust, and seller creativity. Consumer satisfaction with online group buying is predicted primarily by trust, followed by consumer reciprocity. The results suggest that reciprocity, trust, satisfaction, and seller creativity provide considerable explanatory power for intention to engage in online group buying behavior. Vendors who provide online group buying services could diversify the promotion and sales of products.
Limitation of the research was that the user responses in this study were cross-sectional data. Time and resource constraints did not allow the iteration of data collection to observe customer intention over time and determine any long-term effects of the discussed factors on user intention and behavior.
Literature Review
Posting summary of some of the research papers gone through:
Predictors of Online Buying Behavior
The research paper talks about the research project “Wharton Virtual Test Market” and begin with explaining the magnitude and potential of online shopping. It seeks to understand Web consumer demographics, attitudes about online shopping, and predictors of online buying behavior. A survey was conducted asking questions about privacy issues and attitudes about Internet communication and online behavior, as well as routine demographic questions. The result of the survey is summarized as below:
- Surveys agree that the online population is relatively younger, more educated, wealthier, and has fewer African-Americans than the overall U.S. population, although the gaps are gradually closing.
- Although survey respondents report connecting to the Web more frequently at the office and at school, more of their Web-use hours are at home.
- Roughly 42.9% users said they have never bought anything online.
- Looking for product information on the Internet is the most important predictor of online buying behavior.
- As the total number of hours worked by members of a household increases, the less time there is to search for and buy products in the traditional way by, say, visiting brick and-mortar shops.
- Dual-income households seek new ways to find information and buy things that are faster and more convenient.
- The smaller the number of transactions, the more likely a smaller amount of money is involved as well.
The research paper also used a regression model to examine factors predicting annual spending online. For the people who spend more money annually online, regular physical mail is just too slow.
Towards the end of research paper it predicts the reason for lack of online buying. Demographics do not seem to influence whether or not people buy online, nor the amount of money they spend there. Demographics have influence on whether or not a person is online compared with the rest of the population. However, once people are online, whether they buy there has more to do with whether they like being online and whether the time they have for buying things elsewhere is limited.